DVR vs NVR CCTV Guide: Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
In CCTV systems,
DVR (Digital Video Recorder) and
NVR (Network Video Recorder) recorders play central roles. DVRs connect to analog cameras (over coax cables) and digitize the video, while NVRs work with IP cameras over a network. For example, a DVR is “generally used with analog security cameras”, whereas an NVR (Network Video Recorder) is used with digital IP cameras. Understanding their differences helps you pick the best system. Below we explore DVRs, NVRs, their pros and cons, setup basics, and how brands like Avtron support NVR.
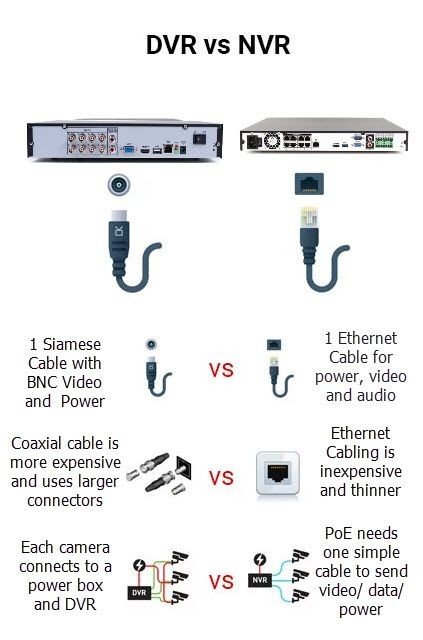
| Feature | DVR (Old Tech) | NVR (New Tech) |
| Camera Type | Analog CCTV | IP Digital Cameras |
| Cable | Coax + Power | PoE (Power + Data in 1 cable) |
| Video Quality | Low to Basic HD | Full HD, 2K, 4K+ |
| Analytics | Recorder-based | AI built into camera |
| Installation | Harder (bulky coax) | Easier (Ethernet/PoE) |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Recommended For | Legacy systems | All modern installations |
What is a DVR and How Does it Work?
A
DVR (Digital Video Recorder) is the classic recorder for analog CCTV cameras. It takes the analog video feed (over coaxial cable) and
converts it into digital files for storage and playback. DVRs often have multiple BNC ports (one per camera). For example, an 8-channel DVR can record eight analog cameras simultaneously. DVRs typically use older compression (H.264, H.265) to save space, and output video to monitors via HDMI or VGA. Many DVRs also support remote viewing over the internet.
- Example: Avtron’s 8-channel DVR (model AT 0808V-L) supports H.264 compression, full D1 (960×480) recording on each channel, HDMI/VGA outputs, up to 4TB HDD storage, and remote web/mobile access. This lets a small business record 8 analog CCTV cams in real time and view them live on a monitor or smartphone.
DVRs are straightforward for existing analog setups. However, note the limitations: the thick coax cables can be hard to install in tight spaces, each camera needs a nearby power outlet, and analog video quality is lower than modern IP cameras. If budget is tight or you have legacy cameras, a DVR system is a “good fit”. But for new, high-definition CCTV projects, NVRs are generally preferred.
What is an NVR and How Does it Work?
A
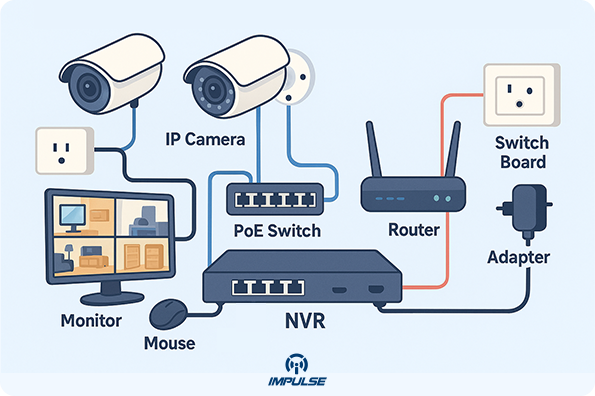
NVR (Network Video Recorder) records IP camera streams. Each IP camera digitizes and compresses the video itself, then sends the data to the NVR over Ethernet or Wi-Fi. The NVR simply stores and manages these digital files. As the guide notes, “an NVR system is used with IP cameras” and records digital video over a network. In practice, an NVR has Ethernet ports (often PoE-enabled) or a WiFi radio to connect cameras.
- Set Up (Wired IP Cameras): Connect your router or PoE switch to the NVR’s network port. Then link each IP camera via Ethernet to the same network (or to the NVR’s PoE ports). Plug a monitor into the NVR via HDMI/VGA and attach a USB mouse. Finally, power on and use the NVR’s interface to auto-detect and add cameras. This streamlined PoE setup means you only need one cable per camera (carrying power and data).
- Set Up (WiFi Cameras): Wireless IP cameras can also work with NVRs. The cameras are battery- or adapter-powered and “video and audio transmission to the network video recorder takes place over WiFi”. In this case, connect the NVR to your router as usual, and ensure the cameras are on the same WiFi network. This allows flexible camera placement without running cables, though stability depends on your wireless signal.
DVR vs NVR: Key Differences
How are DVR and NVR systems different? Here are the main points of comparison:
- Camera type: DVRs work with analog CCTV cameras (traditional coax cameras). NVRs work with IP/digital cameras over Ethernet/WiFi.
- Signal processing: In a DVR, the recorder does the encoding and compression; in an NVR, each camera encodes the video before sending it.
- Cabling: DVRs require coaxial video cables (one per camera) plus separate power lines. NVRs use Ethernet/PoE cables (one cable per camera for data+power) or WiFi. Ethernet is thinner, can carry power, and has no fixed length limit. Analog coax is bulky and limited (~90 m max).
- Video quality: NVR/IP systems generally support higher resolution (1080p, 4K) and higher frame rates, because modern IP cameras are HD and encode on-board. DVRs, limited by analog camera sensors, usually max out at 720×480 (D1) or 1080p if using newer HD-over-coax tech.
- Features: IP cameras (with NVR) often include smart features (motion analytics, PTZ, night vision, AI detection) built into the camera. DVR systems rely on add-on features from the recorder, and analog cams have fewer built-in capabilities.
- Installation distance: Ethernet cables allow very long runs (hundreds of meters with switches, no signal loss). Analog DVRs are limited by cable length.
- Scalability: Adding cameras is usually easier on an NVR – just plug another PoE cable or add a WiFi camera on the network. A DVR system may require a new recorder or infrastructure changes to expand beyond its fixed channels.
- Cost: DVR systems (analog technology) often cost less up front, since analog cams and recorders are cheaper. NVR/IP systems have higher initial cost (cameras and PoE switches) but offer more flexibility and future-proofing. Some guides note DVR can be “good value for older systems”, but NVRs provide better long-term value.
- Compatibility: DVRs using analog standards are quite universal with any analog cam. NVR/IP systems can face compatibility issues if cameras use proprietary protocols – check ONVIF compliance when mixing brands.

CCTV Camera with DVR: Analog Systems Explained
If you have an older CCTV setup, it likely uses analog cameras feeding a DVR. A “CCTV camera with DVR” setup means each camera (with a video BNC output) is connected via coax to the DVR’s input ports. The DVR digitizes and records the feed.
- Example: A small office with 4 analog dome cameras could use an 4-channel DVR to record continuously. Even older systems can output up to 1080p via HD-over-coax on compatible DVRs.
Analog DVR setups are simple but limited. They often have
wired connections (no wireless option unless using analog wireless transmitters). DVR setups require a power source at each camera. Because notes, “coaxial cables are difficult to install in tight spaces”, upgrades often involve running new cable or converters.
DVR Cable Note: DVR installations require careful planning of cable runs. Each camera’s coax and power cable must reach the DVR and a power outlet (or PoE injector). ’s guide warns that DVR systems “are forced to design around nearby power outlets and a maximum cable length of 90 m”. This is why many installers nowadays switch to IP systems.In many modern homes, people upgrade to IP cameras with an NVR for higher resolution and easier setup. But in scenarios where analog cameras are already installed or the budget is tight, a DVR remains “a good fit”. Top DVRs for CCTV (for example Avtron’s models) offer up to 16 channels and features like 3G/WiFi connectivity.
What is an NVR Rack and Channel NVR?
When planning an IP-camera system, two key terms are
“channels” and
“rack” design:
- Channel NVR: The number of channels indicates how many cameras the NVR can handle. A 4-channel NVR supports 4 cameras, an 8-channel supports 8, and so on. For example, a “16-channel NVR” lets you connect up to 16 IP cameras. This scales to large systems – 32, 64, or more channels in professional recorders. Manufacturers (like Avtron) offer NVRs in these channel counts: 8, 16, 32, etc., so you pick one matching your camera count. notes many DVR/NVR systems come in 4, 8, 16, 32 channel versions.
- NVR Rack: In enterprise setups, NVRs are often rack-mountable (1U, 2U height). A rack-mounted NVR fits into a standard 19-inch server rack or cabinet alongside switches and storage. Rack NVRs usually have extra fans and connectors. Using a rack keeps cables organized and allows multiple NVRs or HDD arrays to stack neatly. For example, a large retailer might mount a 16- or 32-channel PoE NVR in a secured 2U rack with RAID drives for redundancy. Even if you use a standalone box NVR, it can be secured on a shelf or in a lockable cabinet (sometimes called a “DVR/NVR rack cabinet”).
Choosing channel count: Think ahead – leave room for extra cams. If you have 10 cameras now but may add more, a 16-channel NVR or DVR is wise. Avtron, for instance, offers dedicated 8-, 16-, and 32-channel NVRs so you can match the system to your site size. 8-channel models suit small offices/homes; 16-channel works for medium businesses; 32-channel and above fit large venues.


How to Set Up a Network Video Recorder
Setup Steps (Wired IP NVR): 1.
Place the NVR: Mount the NVR in a safe, ventilated spot. If it’s rack-mountable and you have a rack, secure it on a rack shelf or mount rails. 2.
Network Connection: Use an Ethernet cable to connect your router (or PoE switch) to the NVR’s network port. Power up the NVR. 3.
Connect Cameras: Plug each PoE IP camera into a PoE switch or the NVR’s PoE ports (if available) via Ethernet. The NVR and all cameras must be on the same local network. 4.
Display & Control: Attach a monitor to the NVR via HDMI or VGA. Connect a USB mouse to the NVR. Power on the monitor. 5.
Initialize Software: Log into the NVR using default credentials. In the NVR menu, go to the Camera/Device Search section and let the NVR find cameras on the network. Add each camera to the system. 6.
Configure: Set the recording schedule, motion detection zones, and storage (HDD) in the NVR settings.
Wireless Setup (WiFi Cameras): If using wireless IP cameras, simply ensure each camera is configured to your WiFi network (via its own setup). The NVR doesn’t need a cable for those cameras – it will see them over the network. The main steps still apply: connect NVR to router, then pair the cameras by adding their IP addresses in the NVR’s interface. This wireless approach “makes installation very simple”, but be mindful of WiFi reliability.
Tips: Always update the NVR firmware and change default passwords. Ensure sufficient hard drive space (e.g. RAID or multiple HDDs for high camera counts). Take advantage of remote features: most NVRs (including Avtron models) support mobile apps or web login for live view and alerts.

NVR WiFi – Using Wireless Cameras
Can NVRs work with WiFi cameras? Yes. Modern NVRs can record streams from WiFi/IP cameras the same as wired ones. As explains, wireless cameras send their video over WiFi to the recorder. In this case, you power the cameras with batteries or adapters, and the NVR only needs to connect to your network.
- Example: A warehouse might install 6 wireless IP cams around the premises. An Avtron NVR with WiFi capability can receive and store all six feeds. This avoids trenching cables but requires strong WiFi coverage. Keep in mind: if the WiFi signal drops, you risk missing footage. For critical systems, a PoE/WiFi hybrid approach (some wired, some wireless) is often safest.
Whether wired or wireless, the key is the network. Make sure cameras and NVR are on the same subnet/VLAN. The setup is largely the same: just add the wireless cameras’ IP addresses in the NVR’s setup menu. Some NVRs even list wireless cameras automatically if they support protocols like ONVIF.
NVR vs Cloud: Note that NVR systems store video locally (on-site), unlike some cloud-based cameras. This ensures no monthly fees and faster local access. If using wireless cams, you still benefit from local storage – the NVR becomes a private cloud for your cameras.
Best DVR and NVR for CCTV
Best DVR for CCTV: Look for DVRs that match your CCTV needs: adequate channels, high resolution support, and reliable storage. Key features include: –
Channels: Pick DVRs with enough channels (8, 16, etc) for your cameras. Avtron, for example, makes 8- and 16-channel DVRs for most setups. –
Video Format: Choose H.265 or H.264 compression for better storage efficiency. –
Remote Access: Ensure the DVR has mobile app or web login for remote viewing (Avtron DVRs support this). –
Outputs: HDMI and VGA outputs allow modern and older monitors to connect. –
Storage: Built-in HDD bays (check maximum TB). Some DVRs offer RAID or expansion (rare for DVRs). –
Extras: Motion alerts, email snapshots, alarm I/O, and multi-language support are useful.A top-notch DVR combines reliability and ease of use. For example, the Avtron AT 0416V-D DVR supports 16 channels, Full HD recording, dual-streaming, remote viewing, and even WiFi connectivity. That kind of spec sheet (8ch, 16ch models) is considered among the best for CCTV DVR systems.
Best NVR for CCTV: Similarly, a good NVR should have: –
PoE Ports: For simplicity, a PoE NVR with built-in switches (e.g. 8 or 16 PoE ports) lets you plug cameras directly. –
Resolution & Analytics: Support for 4K cameras, H.265+, and AI features (face detection, VCA) improves security. –
Storage & RAID: Multiple HDD bays or RAID support ensure you can keep weeks of footage safely. –
Network Bandwidth: High total throughput (e.g. 100+ Mbps) to handle all camera feeds smoothly. –
Compatibility: ONVIF support for third-party cameras, in case you mix brands. –
Ease of Use: Intuitive UI, smart search, and app support.According to industry reviews, the best NVRs allow you to build powerful CCTV without fees. DigitalCameraWorld notes that NVRs are “hubs” for IP cameras and avoid monthly storage fees. Brands like Avtron produce NVRs in the same 8/16/32 channel range. For example, Avtron’s “Monarch” series NVRs boast 4K inputs and AI, making them strong candidates for demanding CCTV.In practice, many recommend PoE NVR kits (camera + NVR bundles) for best value. However, if you want flexibility to choose your cameras and NVR separately, go for reputable models (Hikvision, Dahua, Avtron, Reolink, etc) and compare specs. Real stats show more CCTV systems are IP-based: over 1 billion surveillance cameras were installed in 2023, driving the NVR market up. So modern CCTV designs almost always lean NVR/IP.
Best NVR in India – Context for Avtron
India’s CCTV market is booming. One industry report says the Indian CCTV surveillance sector is worth about
₹9,000 crore (around
$1.1 billion) and growing ~30% per year. That means lots of businesses and homeowners are buying NVR/IP systems. Leading suppliers in India include global names (CP Plus, Hikvision, Dahua, Honeywell, TP-Link) and homegrown brands like
Avtron. Avtron, for example, has been innovating with AI-enabled CCTV and NVRs tailored for India.
What Does “Channel NVR” Mean?
A “channel” in an NVR name refers to how many camera inputs it has. For example: –
8-channel NVR: can connect 8 cameras. –
16-channel NVR: can connect 16 cameras. –
32-channel NVR: can connect 32 cameras. This is why Avtron and other brands sell models labeled “8-channel NVR”, “16-channel NVR”, etc. For instance,
Avtron NVR 8 Channel is an NVR that supports 8 IP cameras,
Avtron NVR 16 Channel supports 16 cameras, and
Avtron NVR 32 Channel supports 32. Basically, each “channel” equals one camera input. As the Reolink guide points out, “a 16 channel DVR [or NVR] enables you to have up to 16 cameras connected to the system”.
Tip: Always choose a few extra channels above your current camera count, for future expansion. If you have 10 cameras now, a 16-channel NVR/DVR is safer than an 8-channel.
Avtron NVR Models – 8, 16, 32 Channels
Avtron offers NVRs in multiple channel configurations:
- Avtron NVR 8 Channel: Ideal for small offices or shops. Supports 8 IP cameras (often up to 4K), with H.265+ compression, PoE ports, and local storage up to several TB. Smaller rack-mount (1U) or desktop boxes.
- Avtron NVR 16 Channel: For larger homes or mid-size businesses. Handles 16 cameras, often at Full HD or 4K. Usually comes with more features like RAID support or AI search, and rack-mountable design.
- Avtron NVR 32 Channel: For big projects (factories, large campuses, malls). Can record 32 cameras simultaneously. These are typically rack-mount units (2U or more) with enterprise features (redundant power, RAID10, etc).

Why Choose Avtron for DVR/NVR?
As a brand,
Avtron specializes in video surveillance (AI cameras, DVRs, NVRs, PA systems). In the context of DVR vs NVR, Avtron covers both: they offer analog DVRs (8/16-ch) and IP NVRs (8/16/32-ch). By reading this guide, you should feel confident: – If you need analog CCTV, Avtron has DVRs with features like HDMI output, dual streaming, and WiFi connectivity. – If you want IP cameras, Avtron’s NVRs provide the scalability and quality discussed above. – Avtron’s focus on AI means their NVRs often come with smart functions (e.g. facial detection, analytics) that enhance a modern security setup. – For the Indian market, Avtron is geared toward local needs (ease of setup, value pricing, multilingual support, 24×7 service centers).
Case in point: In India’s rapid CCTV growth, Avtron serves many retail and educational projects. For example, a 9-acre university campus was secured end-to-end with Avtron AI cameras and NVRs (source: Avtron case studies). Smaller businesses rely on Avtron’s 8-channel NVRs to easily monitor their premises from smartphones. The point is, Avtron NVRs and DVRs are built with the same features our guide highlights: multiple channels, network connectivity, and advanced video quality.
Optimizing Your CCTV System
- Network Video Recorder Setup: As outlined, set up your NVR by connecting it to your router, linking cameras via PoE/WiFi, and configuring in the menu.
- WiFi vs Wired: Use WiFi cameras for flexibility, but favor wired for critical coverage to avoid signal loss.
- Monitoring: Modern NVRs (like Avtron’s) often support dual-screen outputs, mobile apps, and email alerts on motion. Ensure these are enabled for instant awareness.
- Storage Planning: A rule of thumb – more cameras and higher resolution need more storage. Consider 1–4 TB HDDs per 8 channels for 30+ days of video at 1080p.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How many cameras do I need per channel? One camera per channel. An 8-channel NVR/DVR = up to 8 cameras.
- Can I use my old analog cameras on an NVR? Not directly. NVRs record IP streams. You’d need video encoders or converters to turn analog into digital streams.
- Can wireless cameras work with Avtron NVRs? Yes – Avtron NVRs will accept streams from any WiFi-capable IP camera on the same network.
- What if I have both analog and IP cameras? You could run two systems (DVR+NVR) or use hybrid recorders (some HVRs can take both, but Avtron focuses on dedicated DVR or NVR models).
- Do NVRs require internet? No, internet is not needed for basic recording/viewing. Local NVRs store to internal HDD. Internet is only needed for remote access or firmware updates.
Conclusion
Choosing between DVR and NVR depends on your camera type and goals. DVRs are solid for existing analog systems and budget constraints. NVRs are better for new, high-definition CCTV with remote access and analytics. Channels indicate how many cameras you can attach – Avtron offers 8, 16, 32-channel NVRs to match any scale. Wireless NVR setups work too, as long as WiFi is stable.With CCTV market growth booming in India, investing in the right recorder is crucial. Hopefully this guide has helped you understand DVR vs NVR, network setups, and what features to look for (or keyword-search). If you choose an NVR, Avtron’s product line covers NVR with modern capabilities. For example, Avtron’s 8/16/32-channel NVRs come packed with the qualities we discussed: clear video, remote viewing, easy setup, and support for future expansion.